Extended Outcomes of Percutaneous Deep Vein Arterialization: A Two-Year Review
The field of modern vascular treatments is continually evolving, and sometimes the developments come with a mix of excitement and a few confusing bits. In recent years, the procedure known as percutaneous deep vein arterialization has shown promising results in patients suffering from chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI). With a follow-up period of 2 years, the study outcomes give us hope that innovative modalities like the LimFlow System may help patients avoid major amputations and experience significant healing of chronic wounds.
This opinion editorial will take a closer look into the extended follow-up outcomes, the practical aspects of the procedure, and the potential future it holds for those with few conventional treatment options. In doing so, we will use everyday language with the aim to explain the process in a way that is both neutral and informative, much like a Ghostwriter Masterarbeit (help with writing a thesis — Hilfe beim Schreiben einer Masterarbeit) clarifies complex ideas with precision.
Innovative Vascular Treatments: A Promising Alternative
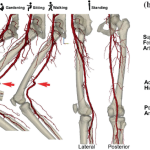
At the heart of this new technique is the idea of converting a vein into an artery to deliver oxygen-rich blood to tissues that have been starved for long periods. By inserting catheters via the groin into a deep artery and through the foot into a deep vein, physicians are able to connect the two using covered stents. This transformation, though surrounded by some tricky parts, offers a more hopeful solution for patients who traditionally faced a dire future with chronic, nonhealing wounds or even major amputation.
Historically, individuals with advanced CLTI ended up with a limited number of treatment options. Many were steered toward amputation due to the overwhelming state of their disease and the nerve-racking nature of surgical interventions. However, with this extended follow-up analysis, a 68% limb salvage rate and significant reductions in pain have emerged as super important data points that suggest a lasting impact. The encouraging survival data and improved wound healing statistics have ignited discussions across the healthcare community about rethinking our approach to these no-option patients.
Building the Bridge: Understanding the Procedure’s Mechanics
For many patients and clinicians alike, the idea of turning a vein into an artery may seem like one of those tangled issues where the details can be quite confusing. To help sort through the fine points of the procedure, let’s break down the process:
How Does the LimFlow System Work?
The LimFlow System essentially acts as a bridge for the delivery of oxygenated blood. Here’s a simplified view:
- Catheter Insertion: One catheter is introduced through a deep artery via the groin while a second is advanced through a vein found in the foot.
- Connection Through Covered Stents: The two catheters are connected behind the knee using covered stents which effectively reprogram the vein into acting like an artery.
- Oxygen Delivery: This new vascular pathway supplies oxygen-rich blood to areas that were previously suffering from prolonged ischemia.
This method is particularly appealing for patients who are not eligible for traditional surgical or endovascular revascularization. By converting the venous structure, the procedure provides a lifeline where none was once available – a direct remedy to the limited options that used to force many patients toward drastic amputation procedures.
Comparing Outcomes Over Time: Short-Term Versus Extended Follow-Up
An important factor in evaluating a new treatment is understanding how the benefits hold over time. In the PROMISE studies, researchers observed that at 6 months, key metrics such as limb salvage and amputation-free survival rates were notably high. Specifically, the limelight was on maintaining limb salvage in a dramatic number of cases and reducing the progression of chronic wounds.
When we look at the extended 2-year follow-up, several points stand out:
- Limb Salvage: At 2 years, 68% of treated patients had not undergone an above-ankle amputation, which is a promising outcome given the advanced state of disease in these individuals.
- Pain Reduction: The median patient-reported pain score dropped from 6 at baseline to 0, underscoring a significant improvement in quality of life.
- Wound Healing: An impressive 71% of wounds were independently judged as healed, with an additional 12% considered to be healing.
Table 1 below offers a side-by-side view comparing the 6-month and 2-year outcomes from these studies:
| Outcome Measure | 6-Month Data | 2-Year Data |
|---|---|---|
| Limb Salvage Rate | 76% (in selected study populations) | 68% (95% CI 60-77) |
| Amputation-Free Survival | 66.1% (in pivotal study) | 49% (95% CI 41-59) |
| Wound Healing (Healed) | – (Preliminary data) | 71% independently adjudicated as healed |
| Pain Score Improvement | Significant improvement relative to baseline | Median score dropped from 6 to 0 |
This table helps us get around the tangled issues of evaluating clinical improvements by offering a clear snapshot of data progression over time.
Patient-Centered Outcomes: Beyond the Numbers
It is critical to note that beyond the clinical statistics, the patient experience plays a super important role in how we evaluate the success of any medical intervention. The real-life improvement for individuals, especially those who were facing the intimidating prospect of major amputation, goes beyond clinical endpoints. Instead, it is measured by quality of life improvements, reduced chronic pain, and the ability to maintain mobility.
Quality of Life and Pain Management
The ultimate goal in treating chronic limb ischemia is not just to extend limb salvage rates but to significantly improve daily living. Prior to receiving the LimFlow therapy, many patients suffered from chronic, nonhealing ulcers that left them with severe pain and reduced mobility. After the procedure, the reduction in median pain scores from a six to a zero on a 10-point scale is nothing short of remarkable. This drastic improvement suggests that patients can enjoy a better quality of life even when confronted with the challenges of a severe medical condition.
Consider these bullet points that summarize the tangible benefits observed post-procedure:
- Pain Relief: Dramatic reduction in self-reported pain levels stabilizes daily functioning.
- Wound Healing: The high rate of wound closure is a key indicator of therapeutic success.
- Enhanced Mobility: With improved limb salvage comes the possibility for enhanced mobility and a reduction in dependency for daily activities.
Psychological and Emotional Benefits
From a patient’s perspective, the psychological burden of facing a major amputation can be both intimidating and overwhelming. The possibility of preserving one’s limb introduces hope where there was previously despair. This psychological boost – the knowledge that there is an alternative to a life-altering amputation – is a quiet triumph that resonates deeply with patients, their families, and care providers.
The Science Behind Deep Vein Arterialization: A Closer Look
Even though the concept might appear shrouded in scientific jargon and technical details, the underlying science is both logical and straightforward. By taking a closer look at how the procedure works, one can appreciate the brilliant simplicity mixed with some challenging parts inherent in the intervention.
Unpacking the Procedure: From Catheterization to Stent Placement
Deep vein arterialization requires precision at every stage. The process involves several key steps:
- Initial Catheter Insertion: Inserting the catheter into a deep artery is a critical and delicate part of the process. Physicians must figure a path through tricky vascular twists and turns to minimize the risk associated with deep vascular access.
- Navigating Through the Venous System: The second catheter travels from the foot, directly into a lesser-used channel – a vein. This is already a significant deviation from the standard revascularization procedure.
- Deployment of Covered Stents: Behind the knee, the catheters are connected using covered stents. These devices serve as conduits, effectively transforming part of the venous system into an arterial pathway. While this approach is still new on the horizon, it represents a critical leap forward, providing oxygen-rich blood to tissues that otherwise would not receive it.
For medical professionals and patients alike, the ability of the procedure to reassign the function of a vein underscores a shift in how we diagnose and address peripheral artery disease complications. The application of covered stents in this uncharted territory not only breathes new life into conventionally challenging cases but also sets the stage for future innovations in vascular medicine.
Data-Driven Insights from Clinical Research
Clinical trials like PROMISE I and PROMISE II are loaded with information that helps practitioners understand both the benefits and some of the complicated pieces of managing CLTI. With the extended study including 137 patients, key insights have been gathered:
- Patient Demographics: The average age of participants was 69–70 years, with a nearly balanced distribution of gender and a significant representation of different ethnic groups. Many of these patients had co-existing conditions such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension, which are common in those with severe vascular disease.
- Clinical Outcome Variables: Aside from amputation-free survival and limb salvage rates, researchers noted improvements in Rutherford classification, a scale that measures the severity of peripheral artery disease. Among patients who maintained their treated limb through 2 years, over half achieved a complete turnaround in their classification, thereby marking a substantial clinical improvement.
- Impact of Stent Patency: The 2-year data showed that patients retaining patency of their stent graft at 3 months had significantly higher limb salvage rates compared to those whose stent patency was lost early. This finding underscores how critical the first few months post-procedure are for long-term success.
These detailed findings allow healthcare practitioners to appreciate the super important role that such innovations may have in treatment paradigms. It also paves the way for improvements in patient selection and procedural modifications in subsequent studies.
Alternative Medicine, Nutrition, and Holistic Management
While the LimFlow System represents a remarkable step forward in interventional procedures, it is equally essential to consider the broader picture of patient care. Chronic limb-threatening ischemia is often accompanied by numerous comorbidities, many of which can be better managed by integrating modern treatments with alternative approaches and thoughtful nutrition.
Embracing a Holistic Approach to Vascular Health
In addition to the immediate benefits provided by advanced medical procedures, a holistic approach can be invaluable. Patients with CLTI typically have multiple health factors at play – from diabetes and high cholesterol to dietary habits and lifestyle choices. Below are several essential strategies that can complement the effects of procedures like deep vein arterialization:
- Nutritional Modifications: Diet plays a key role in the management of vascular diseases. Emphasizing a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, fibers, and healthy fats can help reduce inflammation and promote overall vascular health.
- Regular Physical Activity: Tailored exercise programs, even gentle walking regimens, can aid in improving circulation and maintaining cardiovascular function. Physical activity is a super important component in the management of chronic illnesses.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, counseling, or light physical activities like yoga can help patients cope with the stressful and intimidating reality of living with severe vascular disease.
- Alternative Therapies: Complementary approaches such as acupuncture and herbal supplements may offer additional benefits for some patients. These methods should, however, always be used in conjunction with standard care to ensure safety and efficacy.
By combining cutting-edge interventions like the LimFlow therapy with a comprehensive treatment plan that includes alternative medicine and nutritional guidance, patients can optimize their recovery and overall health outcomes.
Multidisciplinary Care: The Backbone of Success
Successful management of chronic limb-threatening ischemia is not the responsibility of any single discipline. The procedure itself requires the expertise of interventional radiologists, vascular surgeons, and cardiologists. However, the best outcomes are often achieved when there is clear communication and coordination among a multidisciplinary team that includes:
- Primary Care Providers: Overseeing overall patient care and guiding lifestyle adjustments.
- Dietitians and Nutritionists: Tailoring nutritional strategies to improve vascular health.
- Physical Therapists: Designing mobility programs that are safe and effective post-procedure.
- Mental Health Professionals: Providing support as patients deal with both emotional challenges and the physical ramifications of their condition.
This team-centered approach ensures that while modern procedures address the immediate vascular issues, the broader challenges – such as overall health and quality of life – are managed through supportive care strategies. It’s the intersection of advanced treatment and everyday care that truly sets the foundation for long-lasting success.
Weighing the Benefits Against the Risks
No treatment is without risks, and the LimFlow System is no exception. As with any innovative intervention, both patients and practitioners need to be aware of the potential challenges, some of which are compounded by the many twisted issues underlying chronic vascular disorders.
Understanding Common Concerns
The following points summarize the typical apprehensions associated with such procedures:
- Stent Patency: Maintaining the openness of the stent at critical early stages after the procedure is essential. Data indicates that early loss of patency can lead to a lower limb salvage rate.
- Procedure Complexity: Though streamlined in expert hands, maneuvering through the subtle details of vascular access in high-risk patients can be intimidating and is sometimes loaded with complications.
- Patient Selection: The criteria for which patients are most likely to benefit from such advanced procedures are still being refined. There is a need to better fish out and select those who will have the greatest gain.
- Long-Term Durability: While initial clinical improvements are promising, extended follow-up is needed to ensure that benefits such as wound healing and pain alleviation continue over the long stretch of life.
These aspects may appear nerve-racking to patients who are already coping with multiple health challenges. However, ongoing research and careful post-procedural care are aimed at mitigating these risks and ensuring that the benefits far outweigh the potential complications.
Balancing Clinical Benefits With Practical Considerations
As practitioners and policymakers work to integrate this novel intervention into everyday clinical practice, it is crucial to weigh both the positive clinical outcomes and the practical challenges. The following table outlines a balanced view:
| Aspect | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Outcomes |
|
|
| Procedure Aspects |
|
|
| Quality of Life |
|
|
Looking Ahead: Future Perspectives in Limb Salvage Therapy
As we stand on the cusp of what could be a new era in vascular and limb salvage therapy, it’s important to consider what the future might hold. The current data, while promising, are also a call to action to further refine and optimize the procedures. With time, we may be able to reduce even further the risks associated with deep vein arterialization and enhance its overall effectiveness.
Further Research and Technological Innovations
Several areas of further investigation present themselves:
- Device Improvements: The technology behind covered stents and catheter devices can be continually improved through research in materials science and design innovations that reduce the likelihood of early blockage.
- Patient Selection Criteria: As the technique is refined, more nuanced criteria for patient eligibility will help ensure that only those likely to benefit are chosen, reducing the risks of unsuccessful outcomes.
- Multicenter Trials: Larger, randomized controlled studies will help clarify the full scope of benefits and potential pitfalls related to the procedure.
- Integration With Holistic Care: Future studies may also look at how interventions like deep vein arterialization can best be integrated with lifestyle changes, nutritional interventions, and mind-body practices.
Advancements in imaging, procedural technique, and patient monitoring promise to steer through the challenging bits and deliver the kind of precision and safety that modern patients need.
Policy and Healthcare Implications
On a broader scale, the integration of advanced procedures such as deep vein arterialization into standard clinical practice has implications far beyond the immediate clinical results. Healthcare policymakers are tasked with ensuring that state-of-the-art treatments are accessible, safe, and cost-effective. The extended follow-up data add another layer of evidence that may influence how healthcare systems approach vascular diseases, particularly in patients who have exhausted conventional options.
Some key points for policymakers include:
- Reimbursement Policies: The cost associated with these novel procedures needs to be balanced against potential savings from avoided amputations and reduced long-term healthcare costs.
- Training and Certification: Surgeons and interventional radiologists must receive proper training to figure a path safely through the technical aspects of deep vein arterialization.
- Patient Education: Information campaigns are essential, ensuring that patients are fully aware of both the benefits and the potential risks as they face decisions regarding their treatment options.
Conclusion: A New Light on Limb Salvage and Quality of Life
In conclusion, the two-year follow-up results of percutaneous deep vein arterialization provide a hopeful outlook for patients with end-stage CLTI who were once considered beyond the reach of effective therapy. The reported improvements in limb salvage rates, wound healing, and pain reduction represent a dramatic shift that can change the lives of many. Although the procedure comes with its own set of intimidating challenges and complicated pieces, the overall benefits seem to tip the balance in favor of its continued development and integration into modern treatment paradigms.
From an editorial standpoint, it is super important to recognize that medical innovation rarely comes without its twists and turns. However, every step forward brings with it the potential to save lives and significantly improve quality of life. The data suggest that what was once seen as a desperate measure – a procedure aimed at rescuing a limb that might otherwise be lost – could become a standard of care for those with few options. With further studies, refinement of techniques, and a multi-pronged approach that includes nutrition, alternative care, and comprehensive rehabilitation, the promise of percutaneous deep vein arterialization looks poised to fulfill its early promise.
For patients, clinicians, and policy makers alike, this is an exciting time. As research and clinical practice continue to work through the little details and subtle parts of this innovative procedure, there is genuine optimism that many lives will be transformed for the better. While there remain some nerve-racking and full-of-problems aspects to manage, the journey ahead is equally full of potential breakthroughs that could redefine the management of chronic limb-threatening ischemia.
To summarize the key takeaways:
- Significant Limb Salvage: A 68% limb salvage rate at 2 years is a meaningful improvement for patients who otherwise faced imminent amputation.
- Enhanced Wound Healing: With 71% of wounds adjudicated as healed, the procedure offers a tangible benefit in overcoming chronic, nonhealing ulcers.
- Pain Reduction: The drop in median pain scores from 6 to 0 underscores not only a technical success but also a profound improvement in quality of life.
- Holistic Integration: Combining advanced surgical intervention with alternative medicine, nutritional guidance, and multidisciplinary team care can provide the best overall outcomes.
As we continue to figure a path through both the straightforward and nerve-racking elements of vascular interventions, the story of deep vein arterialization remains a testament to the ingenuity of modern medicine. It teaches us that even in the face of severe conditions loaded with issues, innovation can open doors to new possibilities, delivering hope and a better future to those in need.
Ultimately, this journey is about more than clinical statistics. It’s about restoring dignity, improving independence, and ensuring that advances in medical science translate into real-world improvements for patients. The extended promise of the LimFlow System is one step in a larger mission – to offer care that is as comprehensive as it is cutting edge, and to continuously seek out new solutions for the pressing health challenges of our time.
In light of these insights, the path ahead seems promising for chronic limb-threatening ischemia patients. With ongoing research, patient education, and a collaborative approach among healthcare professionals, we are witnessing a turning point in the management of a condition that was once deemed nearly intractable. Whether it’s through advanced interventional procedures or integrated holistic care, the future of vascular treatment is bright, driven by science, compassion, and an unwavering commitment to patient well-being.
As we take a closer look at this evolving narrative, it’s clear that while the journey may still present some overwhelming and tangled issues, the end goal of preserving limbs and improving lives remains our primary rallying cry. This editorial, while based on current evidence, ultimately serves as a reminder that progress in medicine is always a work in progress – one that is enriched by dedication, research, and an unwavering focus on the patient’s quality of life.
Originally Post From https://www.medpagetoday.com/cardiology/interventionalcardiology/118250
Read more about this topic at
Innovative Endovascular Approach for Limb Salvage in …
Real-World Lower Extremity Revascularization Strategies